What is Holography
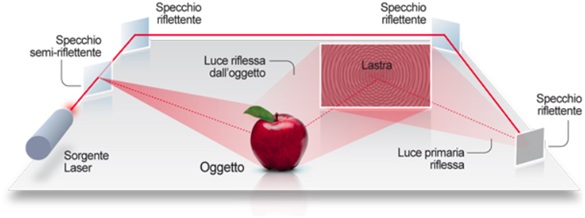
Holography is a technology aimed at the storage and subsequent reproduction of three-dimensional optical information through the recording of a fine interweaving of interference differences on a suitable holographic plate or film.
The fringes are generated by the encounter of a coherent light beam (e.g. laser beam), called beam or reference wave , with the wave front diffused by a object illuminated by the same coherent beam, called object wave .
The plates (typically consisting of silver halides), after being chemically developed, can diffract a coherent beam of light equal to the reference wave used to create the hologram, reconstructing the desired object wave.
Compared to traditional photography, in which a lot of information relating to the photographed object is lost, holography is able to return a virtual image with depth and perspective characteristics of the three-dimensionality of the object.
The aforementioned "three-dimensionality" attributed to the holographic image must be understood as the "parallax effect of the image".